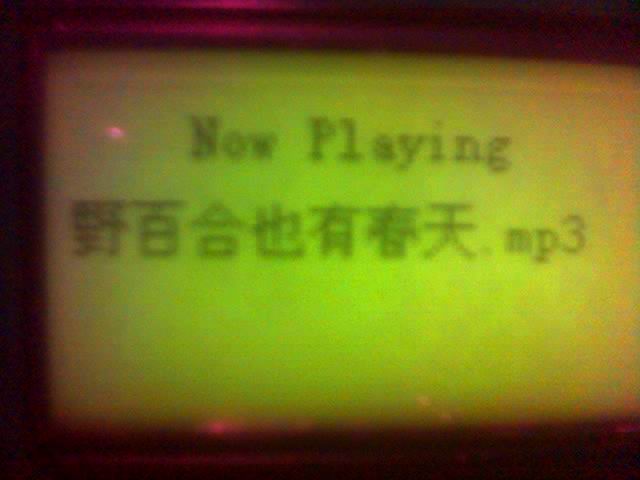
经过几天的摸索终于可以显示mp3的中文名了。
现在将我做的资料与大家分享,想做mp3的朋友可以试试。
点击此处下载armok01141262.rar
上面的文件是我在网上搜索的素材,我自己编了些小程序将其转换成两张表,即unicode与gbk相互转换的表。
点击此处下载armok01141263.rar
上面是我用程序产生的GBK字符,是按照顺序存放的,用这个文件配合我前几天发的“GB2312字库制作方法”中的程序用于生成GBK字库点阵。
点击此处下载armok01141264.rar
上面的文件是我最终生成的用于mp3的4个文件了。
st12.sys为gbk字库12*12的点阵文件,取模方式 “纵向取模,高位在下”(我用的液晶是128*64 ks0108兼容LCD模块)
st16.sys为gbk字库16*16的点阵
以上两个文件的起始汉字是以0x8140 开始的,为了在程序中能线形查找,其中不存在的编码 如0x**7f 0x**ff等均在编码内,只不过不会用到。也就是说从0x8140 ~0xfeff 其中高位从0x81到0xfe 地位从0x40到0xff 即126*192 = 24192个汉字数据。
因此12*12的点阵文件大小是580608Bytes (每个汉字用24字节,汉字下半截虽用4bits但是存储是按8bits)
16*16的点阵文件大小是774144Bytes(每个汉字用32字节)
uni2gbk.sys为unicode转gbk的表,从unicode的0x4e00 到0x9fa5 顺序存放着相应的gbk码,总共20902个汉字,对应的文件是41804Bytes
注:由于没有找到一些符号的unicode对照表,因此这张表中只包含了汉字部分。因此不能显示诸如“”()等符号,程序中要做相应处理。
注文件存放方式是高字节在前 比如0x4e00 存放方式为0x4e 0x00
gbk2uni.sys为gbk转unicode的表,从gbk的0x8140 到0xfeff 即126*192 = 24192按照gbk的编码顺序放,为了线形查找,其中不合法的或根据资料没有相应unicode码的都作了填零处理。文件大小为48384Bytes
注文件存放方式是高字节在前 比如0x4e00 存放方式为0x4e 0x00
用的时候要把上面的4个文件拷贝到sd卡中或u盘中,注意为了程序好处理不要让这4个文件产生碎片,要连续的存放,最好的方法是格式化后再把这几个文件拷过去。
下面说说如何在程序中处理
首先是初始化:
#include"LCD_GBK.h"
unsigned long GBK12,GBK16,GBK2UNI,UNI2GBK;//用于存放四个文件的起始扇区
extern unsigned long FirstDataSector;//第一个数据扇区
extern unsigned int SectorsPerClust;//每簇扇区数
extern unsigned int BytesPerSector;//每扇区字节数
unsigned char GBK_Buffer[32];//单个汉字点阵数据缓冲
unsigned char GBK_Ini()//gbk初始化
{
GBK12 = FAT_Open("\\st12.sys");//打开文件,得到簇号
if(GBK12 == 1)return 1;
GBK16 = FAT_Open("\\st16.sys");
if(GBK16 == 1)return 1;
GBK2UNI = FAT_Open("\\gbk2uni.sys");
if(GBK2UNI == 1)return 1;
UNI2GBK = FAT_Open("\\uni2gbk.sys");
if(UNI2GBK == 1)return 1;
//将簇号转成扇区号
GBK12 = (unsigned long)FirstDataSector+(unsigned long)(GBK12 - 2)*(unsigned long)SectorsPerClust;//calculate the actual sector number
GBK16 = (unsigned long)FirstDataSector+(unsigned long)(GBK16 - 2)*(unsigned long)SectorsPerClust;//calculate the actual sector number
GBK2UNI = (unsigned long)FirstDataSector+(unsigned long)(GBK2UNI - 2)*(unsigned long)SectorsPerClust;//calculate the actual sector number
UNI2GBK = (unsigned long)FirstDataSector+(unsigned long)(UNI2GBK - 2)*(unsigned long)SectorsPerClust;//calculate the actual sector number
return 0;
}
这样可以得到四个文件的起始扇区,接下来的操作在此基础上加上偏移量就可以了,无须再次寻找文件。
其中FAT_Open("\\st12.sys");//打开文件,得到簇号
该函数实现寻找根目录下st12.sys的起始簇,这个FAT函数可以搜索一下我以前发的帖子,那里有完整的程序。
根据汉字内码找其点阵数据:
unsigned char Read_One_GBK16(unsigned char *ch)
{
unsigned int temp1;
unsigned char temp2;
unsigned int sector_offset;//扇区偏移
unsigned int byte_offset;//字节偏移
unsigned char buffer[512];
temp1=*ch;
temp2=*(ch+1);
if(temp1<0x81||temp2<0x40)return 1;//不合法的汉字
temp1-=0x81;//的到类似于2312的区号
temp2-=0x40;//位号
temp1*=192;//xx7f and xxff are included
temp1+=temp2;//得到偏移
//temp1*=24;
sector_offset = temp1/(BytesPerSector/32);//算出要读哪个扇区
byte_offset = (temp1%(BytesPerSector/32))*32;//算出要读扇区的哪个字节
if(FAT_ReadSector(GBK16 + sector_offset,buffer))return 1;//读要读的扇区
for(temp2 = 0,temp1 = byte_offset;temp2<32;temp2++,temp1++)GBK_Buffer[temp2] = buffer[temp1];//复制要复制的数据
return 0
}
注意由于在设计时非法的编码如0x**7f与0x**ff都计在内所以每个区有192个汉字,而不是190个
这是16*16的程序
12*12的程序稍复杂一点,因为512/24 不能除尽,因此还要判断是不是有数据在下一个扇区。其代码如下(没加注释)
unsigned char Read_One_GBK12(unsigned char *ch)
{
unsigned long temp1;
unsigned char temp2;
unsigned int sector_offset;
unsigned int byte_offset;
unsigned char buffer[512];
temp1=*ch;
temp2=*(ch+1);
if(temp1<0x81||temp2<0x40)return 1;
temp1-=0x81;
temp2-=0x40;
temp1*=192;//xx7f and xxff are included
temp1+=temp2;
temp1*=24;
sector_offset = temp1/BytesPerSector;
byte_offset = temp1%BytesPerSector;
if(FAT_ReadSector(GBK12 + sector_offset,buffer))return 1;
if(byte_offset>488)
{
for(temp2 = 0,temp1 = byte_offset;temp2<(BytesPerSector - byte_offset);temp2++,temp1++)GBK_Buffer[temp2] = buffer[temp1];
if(FAT_ReadSector(GBK12 + sector_offset + 1,buffer))return 1;
for(temp1 = 0;temp2<24;temp2++,temp1++)GBK_Buffer[temp2] = buffer[temp1];
}
else for(temp2 = 0,temp1 = byte_offset;temp2<24;temp2++,temp1++)GBK_Buffer[temp2] = buffer[temp1];
return 0;
}
至于显示我就不说了,不同的液晶操作不同,只要把读出的数据按照你的LCD的操作方法写进去即可。
unicode到gbk的转换。
unsigned char Unicode_to_GBK(unsigned char *ch)
{
unsigned int temp;
unsigned int sector_offset;//扇区偏移
unsigned int byte_offset;//字节偏移
unsigned char buffer[512];
temp = *((unsigned int*)ch);//由于FAT中文件民unicode码是 地字节在前,所以要按uint型读
temp -= 0x4e00;//减去基础数据
temp *= 2;//每个汉字两个字节
sector_offset = temp/BytesPerSector;//计算出扇区偏移,确定存在哪个扇区
byte_offset = temp%BytesPerSector;//存在哪个字节
if(FAT_ReadSector(UNI2GBK + sector_offset,buffer))return 1;//读那个扇区
*ch = buffer[byte_offset];//将数据读出
*(ch+1) = buffer[byte_offset+1];
return 0;
}
要注意的是FAT中文件名的存放方式是低字节在前,而gbk的存放是高字节在前,操作时不要搞混了。
gbk到unicode的转换mp3种用不着所以我也就没试过,程序也没写,因此那四个文件,gbk2uni.sys可以不拷。
由于资料有限unicode的编码只有汉字部分 即所谓的“中日韩统一汉字编码”,(2w多汉字)显示汉字肯定是没问题了,有些符号没有。希望大家去完善一下。
谢谢ouravr的各位朋友!
来几张图片
试验用的板子(已经在这出现好多次了)
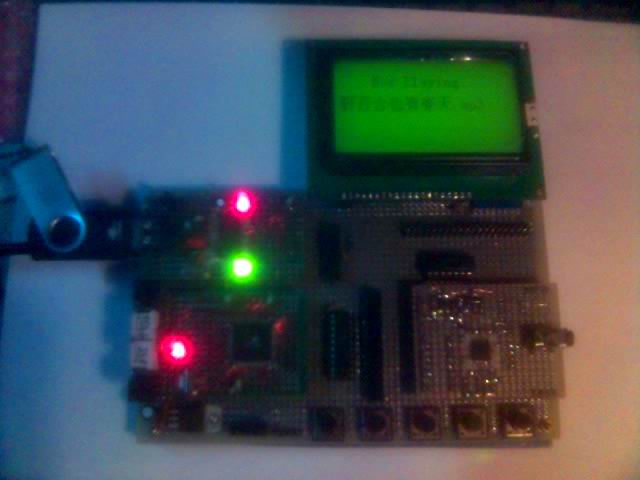

显示中文名

|